As we navigate 2025, a new COVID-19 variant (currently designated JN.1.XX by global health authorities) has emerged, prompting understandable questions for travelers. While vigilance is key, panic isn’t necessary. Here’s what you need to know to travel smartly and safely:

1. What We Know About the JN.1.XX Variant
- Origin & Spread: Descended from the Omicron lineage (like the previous JN.1 variant), JN.1.XX demonstrates increased transmissibility. It’s rapidly becoming dominant in multiple regions.
(World Health Organization (WHO) – Tracking Variants) - Symptoms: Reports suggest symptoms remain similar to recent Omicron variants: primarily upper respiratory (runny nose, sore throat, cough, fatigue, headache). Loss of taste/smell is less common. Severity appears generally mild-to-moderate for most vaccinated individuals, but can vary.
- Vaccine/Efficacy: Current evidence indicates updated 2024-2025 COVID-19 vaccines continue to provide significant protection against severe disease, hospitalization, and death from JN.1.XX. Protection against infection may wane over time.
(CDC – Stay Up to Date with COVID-19 Vaccines)
2. Current Travel Restrictions & Requirements (June 2025)
The landscape is fluid! Rules vary significantly by country and can change rapidly:
- Testing: Some destinations may reinstate pre-departure or arrival testing requirements, particularly for unvaccinated travelers. Always check before you book and immediately before travel.
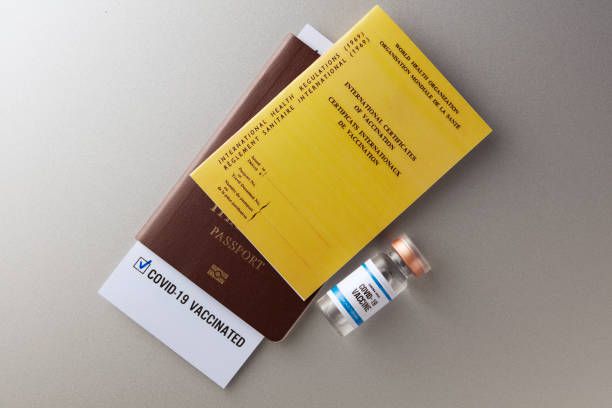
(Kayak Travel Restrictions Map) - Vaccination Proof: While many countries lifted mandates, some may require proof of vaccination (especially the latest booster) or recovery for entry. Carry digital/physical copies.
- Quarantine: Targeted quarantine rules may apply for symptomatic arrivals or those testing positive. Know your destination’s policy.
- Mask Mandates: Airline and airport policies vary. Some countries or specific settings (hospitals, public transport) might still require masks. Pack high-quality masks (N95/KN95/KF94).
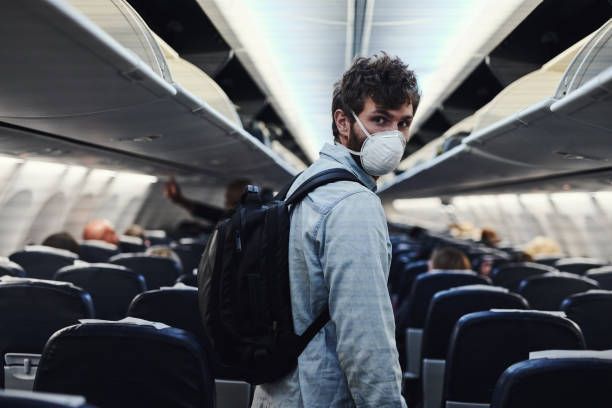

3. Essential Precautions for Travelers
- Get Boosted: The single most important step. Ensure you’ve received the latest 2024-2025 COVID-19 booster designed to target recent variants. Allow 2 weeks for full effect before travel.
(Find Vaccines – Vaccines.gov) - Pack a Travel Health Kit: Include high-quality masks, rapid antigen tests, hand sanitizer (>60% alcohol), and basic fever/pain relievers.
- Consider Travel Insurance: Choose a policy covering COVID-19-related medical expenses and trip interruptions/cancellations. Read the fine print carefully.
- Test Strategically: Test yourself before meeting vulnerable individuals or joining group tours. Test if you develop symptoms during travel.
- Prioritize Air Quality & Hygiene: Choose well-ventilated spaces when possible. Maintain good hand hygiene, especially before eating/touching your face.
- Have a Contingency Plan: Know what to do and where to go if you test positive abroad (isolate, seek medical care, contact accommodation/airline, understand local isolation rules).

4. Staying Informed is Crucial
- Destination-Specific Rules: ALWAYS check official government sources for your destination country and any transit countries shortly before departure:
- Airline & Airport Policies: Check your airline’s website for specific COVID-19 requirements (masking, testing, forms).
- Reputable Health Sources:
Travel Smart, Travel Safe
The emergence of JN.1.XX is a reminder that COVID-19 remains part of our global health landscape. By staying updated on vaccinations, diligently checking travel requirements, packing smartly, and staying informed through official channels, travelers can significantly mitigate risks. Responsible travel—protecting yourself and others—remains paramount. Enjoy your adventures, but do so with awareness and preparation.

Disclaimer: This information is current as of June 2025. COVID-19 regulations and variant situations evolve rapidly. Always consult official government and health organization sources immediately before and during travel for the absolute latest requirements and guidance.
Dr. Mohammad Rizwan Feroz