Ah, the dream trip. Exotic sights, tantalizing smells, unforgettable experiences… and then, it hits. That urgent rumble, the sprint to the bathroom, the feeling your insides are staging a rebellion. Traveller’s Diarrhea (TD) – the unwelcome souvenir nobody wants. At DoctorTravelLog, we’ve seen it all (and treated it all!), and we’re here to arm you with knowledge, not just fear. Let’s demystify this common travel woe.

What Exactly Is This Gut Rebellion?
Simply put, TD is your digestive system throwing a tantrum after encountering unfriendly bacteria, viruses, or parasites it’s not used to. Think E. coli, Salmonella, Campylobacter, norovirus, or Giardia. These microscopic hitchhikers usually enter via contaminated food or water. While rarely life-threatening for healthy adults, it can turn paradise into a porcelain prison for 3-7 days.
Why Me? The Usual Suspects:
- The Water: Even tiny amounts of contaminated water used to wash salad, ice cubes in your drink, or brushing your teeth can be the culprit. “Local water” doesn’t just mean tap; be wary of sources.
- The Food: Undercooked meats (especially street food), raw seafood, unpasteurized dairy, and anything washed in contaminated water (fruits, veggies) are prime offenders. Buffets where food sits out are risky.
- Person-to-Person: Poor hand hygiene after using the bathroom or before eating spreads germs fast.
- Location Matters: Risk is highest in parts of Asia (especially South and Southeast Asia), Africa, Latin America, and the Middle East. But anywhere with different sanitation standards poses some risk.

Recognizing the Enemy: Symptoms Beyond the Obvious
- Urgent need to go
- Abdominal cramps and bloating
- Nausea and sometimes vomiting
- Low-grade fever
- General malaise (feeling awful)
- Loss of appetite
Doctor’s Note: Blood in stool, high fever, severe pain, or dehydration (dizziness, extreme thirst, little/no urination) are RED FLAGS. Seek medical help immediately.
Your Best Defense: Prevention is King (and Queen!)
You can significantly reduce your risk. Think like a germ detective:
- Hydrate Smart:
- Bottled/Sealed: Drink only commercially bottled water with intact seals. Check the cap!
- Boiled: Vigorously boiled water (1 minute, 3 mins at altitude) is safe.
- Purified: Use reliable water filters (check pore size – 0.1-0.4 microns for bacteria/protozoa) or chemical purification (chlorine dioxide tablets) following instructions exactly.
- Avoid Ice: Unless you know it’s made from purified/bottled water. Assume it’s not.
- Hot Drinks: Generally safe (coffee, tea made with boiling water).
- Toothbrushing: Use bottled or purified water.
- Eat Wisely (“Boil It, Cook It, Peel It, or Forget It!”):
- Peel It Yourself: Bananas, oranges, mangoes = usually safe. Avoid pre-cut fruit or salads.
- Hot & Steamy: Eat foods served piping hot, straight from cooking. Avoid lukewarm buffet items.
- Skip the Risky: Raw or undercooked meats, fish, shellfish. Unpasteurized milk, cheese, yogurt. Street food, unless you see it cooked thoroughly right in front of you and served hot.
- Dry & Packaged: Breads, chips, factory-sealed items are generally low risk.
- Condiments: Be wary of open sauces sitting out.
- Hand Hygiene is Non-Negotiable:
- Wash hands thoroughly with soap and safe water (or use alcohol-based hand sanitizer with >60% alcohol if soap/water unavailable) BEFORE eating, AFTER using the bathroom, and after touching potentially contaminated surfaces.
- Carry hand sanitizer everywhere.
- Consider Prophylaxis (Cautiously):
- Bismuth Subsalicylate (Pepto-Bismol): Taking it preventatively (e.g., 2 tabs 4x/day) can reduce risk by ~50%, but isn’t suitable for everyone (aspirin allergy, pregnancy, kids, certain meds). It turns your tongue black!
- Antibiotics: Generally NOT recommended for prevention due to side effects and antibiotic resistance. Reserved for high-risk individuals (weakened immune system, critical trips) only after consulting a travel doctor.

When Prevention Fails: Weathering the Storm
Even the most careful traveler can get hit. Don’t panic! Focus on:
- Hydration, Hydration, Hydration: This is CRITICAL. You’re losing fluids fast.
- Oral Rehydration Solution (ORS): The GOLD STANDARD. Packets are cheap, light, and lifesaving. Mix with SAFE water. Sip constantly. Tastes bland? Add a splash of safe juice.
- Safe Fluids: Bottled water, clear broths, weak tea. Avoid caffeine, alcohol, sugary drinks (soda, juice) – they can worsen diarrhea.
- Signs of Dehydration: Dizziness, dark urine, dry mouth, lethargy. Push ORS hard!
- Diet: Listen to Your Gut (Gently)
- Initially: Focus on fluids. The BRAT diet (Bananas, Rice, Applesauce, Toast) is outdated advice. Bland, starchy foods (plain rice, crackers, noodles) are okay if tolerated, but hydration is paramount.
- Gradually Reintroduce: As you feel better, add simple proteins (boiled chicken, plain yogurt if tolerated) and cooked veggies. Avoid greasy, spicy, or high-fiber foods initially.
- Over-the-Counter Relief:
- Loperamide (Imodium): Helps slow down the plumbing for adults. Useful for long bus rides/flights. BUT: Do NOT use if you have fever, bloody stools, or severe abdominal pain – it can trap the bug inside. Use only for symptom control, not as a cure. Follow dosing.
- Bismuth Subsalicylate (Pepto-Bismol): Can help reduce symptoms and shorten duration slightly.
- When Antibiotics Are Needed:
- For moderate to severe TD (frequent stools, fever, blood, incapacitation), antibiotics prescribed before your trip by a travel doctor can be a game-changer, shortening illness significantly (often 1-3 days).
- Common options: Azithromycin, Rifaximin (less absorbed, good for certain bacteria). Crucial: Take exactly as prescribed. Never use leftover antibiotics.

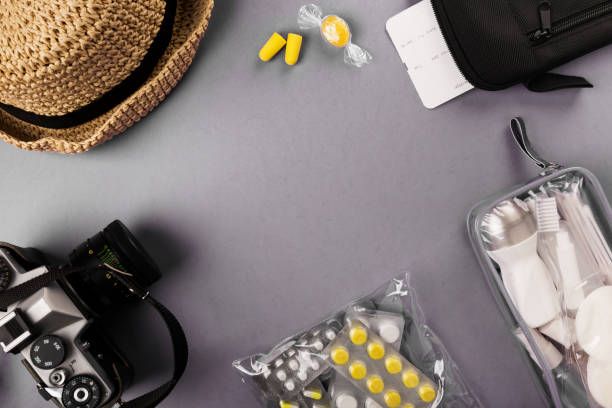
Doctor’s Bag Must-Haves:
- Oral Rehydration Salts (ORS) packets
- Loperamide (Imodium)
- Bismuth Subsalicylate (Pepto-Bismol)
- Antibiotic prescribed by your travel doctor (if recommended)
- Alcohol-based hand sanitizer (>60% alcohol)
- Thermometer
- Basic first-aid supplies
Special Cases: Kids, Pregnancy, Chronic Conditions
- Children: Dehydrate much faster. ORS is vital. Consult a doctor immediately for infants/young children or severe symptoms. Antibiotic choices differ.
- Pregnancy: Prevention is even more critical. Consult your OB/GYN and a travel medicine specialist well before travel. Treatment options are more limited.
- Weakened Immune Systems/Conditions: Higher risk for severe illness. Essential to see a travel medicine specialist for a personalized plan.
The DoctorTravelLog Bottom Line:
Traveller’s Diarrhea is incredibly common, often manageable, but definitely disruptive. Respect the risks, prepare diligently, but don’t let fear ruin your adventure.
- Prevention Focus: Water, food, hands. Be vigilant.
- Hydration is Key: Pack ORS and use it at the first sign.
- Know When to Treat: Have OTC meds and know when prescribed antibiotics are needed.
- Seek Help for Red Flags: Don’t hesitate if things get severe.
With smart preparation and the right knowledge, you can significantly reduce your chances of getting TD and handle it effectively if it strikes. Now, go explore confidently! Stay safe, stay hydrated, and happy travels from the team at DoctorTravelLog.
Dr. Wanderlust (aka Dr Mohammad Rizwan Feroz/DoctorTravelLog)
Helping you explore the world, one healthy step at a time.