An ER Doctor in Muscat Explains the Critical Difference
As an emergency physician working in Muscat, I see firsthand the confusion surrounding the terms “heart attack” and “cardiac arrest.” Often used interchangeably, they describe two distinct, though sometimes related, life-threatening events. Understanding this difference isn’t just medical jargon – it can be the difference between life and death. Knowing what to look for and how to react is crucial.

The Core Difference: Plumbing vs. Electricity
Think of your heart as a house:
1. Heart Attack (Myocardial Infarction): A Plumbing Problem
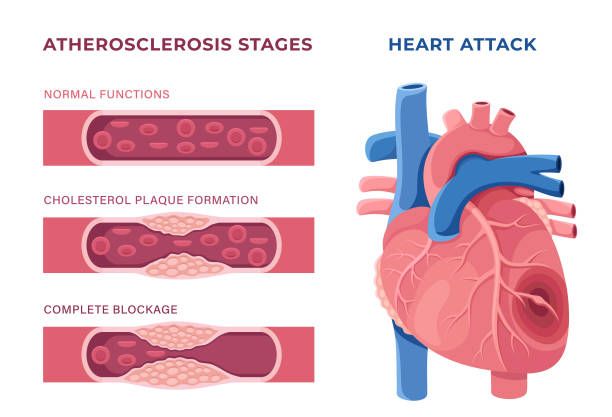
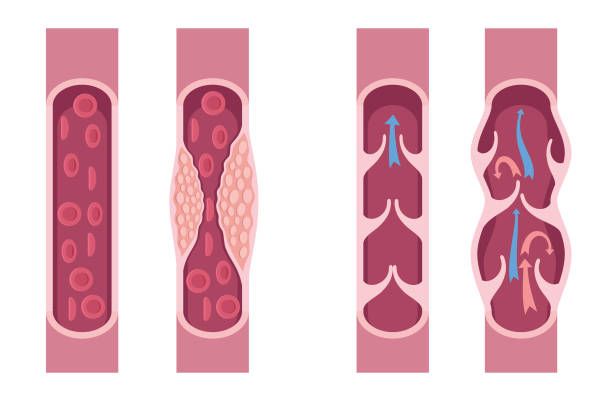
- What Happens: A blocked pipe! One or more coronary arteries supplying blood to the heart muscle itself become obstructed, usually by a blood clot forming on top of a cholesterol plaque. This blockage cuts off oxygen-rich blood to a section of the heart muscle.
- Analogy: A clogged pipe preventing water from reaching a specific room. That room (heart muscle) starts to suffer damage.
- The Heart: Usually still beating. The problem is blood flow to the heart muscle.
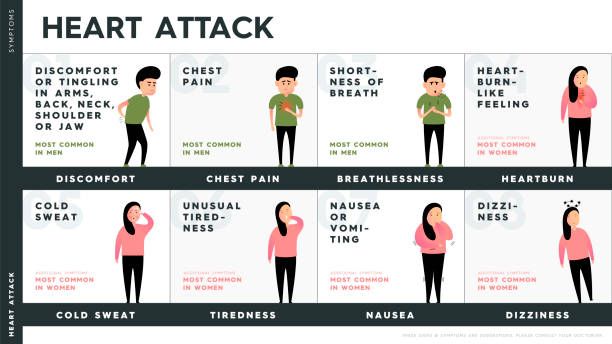
- Symptoms (Often Gradual, Can Last Hours/Days):
- Chest pain, pressure, tightness, or squeezing (like an elephant sitting on your chest)
- Pain radiating to arm(s), neck, jaw, shoulder, or back
- Shortness of breath
- Cold sweat
- Nausea/vomiting
- Lightheadedness
- Unusual fatigue
- (Important Note: Symptoms can be subtle, especially in women and diabetics – don’t ignore unusual feelings!)
- Outcome Without Treatment: The affected heart muscle begins to die. This damage can weaken the heart, lead to heart failure, or trigger a cardiac arrest.
2. Cardiac Arrest: An Electrical Problem
- What Happens: A sudden power outage! The heart’s electrical system malfunctions, causing the heart to beat chaotically (ventricular fibrillation) or stop beating altogether (asystole). This halts effective pumping. Blood stops flowing to the brain, lungs, and other vital organs.
- Analogy: The house’s electrical system shorts out, plunging everything into darkness and stopping all function instantly.
- The Heart: Stops beating effectively or stops completely. No pulse. No blood flow.
- Symptoms (Sudden and Dramatic):
- Sudden collapse
- Loss of consciousness/unresponsiveness
- No normal breathing (may have gasping agonal breaths)
- No pulse
- Outcome Without Immediate Treatment: Death within minutes. Brain damage starts after just 4-6 minutes without blood flow.

The Critical Link: How One Can Lead to the Other
- A severe heart attack can cause an electrical disturbance that triggers cardiac arrest.
- Other conditions like severe arrhythmias, electrocution, drowning, trauma, or respiratory failure can also cause cardiac arrest without a preceding heart attack.
Why This Difference Matters in Muscat (and Everywhere Else)
1. Recognition:
Knowing the symptoms helps you identify the problem faster. Chest pain demands urgent medical attention before it might turn into arrest. Unresponsiveness and no breathing is cardiac arrest now.
2. Response:
- Heart Attack: Call Emergency Services Immediately (999 in Oman). Every minute of delay means more heart muscle damage. Chew aspirin (if not allergic) as advised while waiting for help. Do NOT drive yourself.
- Cardiac Arrest:This is an absolute emergency requiring instant action:
- Shout for Help & Dial 999.
- Start CPR (Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation) IMMEDIATELY: Push hard and fast (at least 5-6 cm deep, 100-120 beats per minute) in the center of the chest. Don’t stop until help arrives or an AED is ready.
- Use an AED (Automated External Defibrillator) if available: Turn it on and follow the voice prompts. These devices can shock the heart back into a normal rhythm and are increasingly available in public places in Muscat. CPR + AED use within the first few minutes is the ONLY chance for survival.

Prevention: Your Best Defense
While not always preventable, managing risk factors significantly lowers your chances:
- Control Blood Pressure & Cholesterol
- Manage Diabetes
- Quit Smoking/Vaping
- Maintain a Healthy Weight
- Exercise Regularly
- Eat a Heart-Healthy Diet (Mediterranean style is excellent)
- Manage Stress
- Attend Regular Health Check-ups

The Bottom Line from the Muscat ER:
A heart attack is a circulation problem – blood flow to the heart is blocked. The person is usually conscious and experiencing symptoms. Call 999 immediately.
Cardiac arrest is an electrical problem – the heart stops beating effectively. The person is unconscious, not breathing normally, and has no pulse. This requires immediate CPR and an AED. Call 999 and START COMPRESSIONS NOW.
Understanding this difference empowers you to act swiftly and correctly. Share this knowledge. Encourage CPR training – it’s a lifesaving skill anyone can learn. Your actions in those critical first minutes before help arrives here in Muscat can make all the difference.
👍 Found this helpful? Show some love & follow us on Instagram @doctortravellog for expert tips & fresh updates!
💬 Got thoughts or questions? React below or drop a quick comment — no login needed!
❤️ 😮 🤔 👍 👎